.webp)
Here are today’s most important updates from the realm of Science and Space.
Life on Mars? NASA’s New Study Suggests It Could Be Hiding Below the Ice
NASA researchers believe that meltwater beneath Martian ice could possibly support microbial life. “If we’re trying to find life anywhere in the universe today, Martian ice exposures are probably one of the most accessible places we should be looking,” said the paper’s lead author, Aditya Khuller of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Mars harbours two types of ice: frozen water and frozen carbon dioxide. Based on computer modeling, the research has shown that the amount of sunlight that can shine through water ice would be sufficient for photosynthesis to occur in shallow pools of meltwater below the surface of those icy structure. Meanwhile, life started in similar environment on the Earth billions of years ago.
Unlocking the Secrets of Skin: First Human Skin Map Unveiled

For the first time, scientists from Wellcome Sanger Institute and Newcastle University have prepared a human skin map providing a ‘recipe’ to geney skin and possibly help preventing scar formation. This map will help in understanding how skin forms before birth, and what goes wrong in disease.
Dr Elena Winheim, co-first author of the study said: “These insights have amazing clinical potential and could be used in regenerative medicine, when offering skin and hair transplants, such as for burn victims or those with scarring alopecia.”
The largest organ of the human body, skin, measures approximately two square metres, providing a protective barrier, which is essential for body temperature regulation.
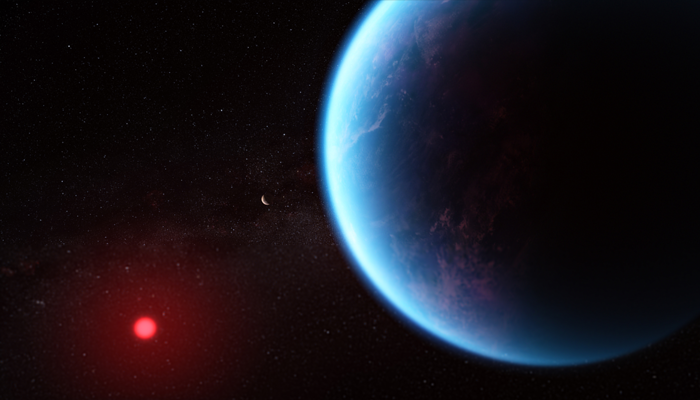
Galactic Mystery: Scientists Probe Star System for Alien Life Signals
It’s a TRAP(PIST)-1! 🦑
— NASA (@NASA) May 4, 2023
About 40 light-years away lies a planetary system with the most Earth-sized exoplanets found in a star's habitable zone. Learn more about the TRAPPIST-1 system that was recently studied by @NASAWebb: https://t.co/0sxJaVq7RB#MayTheFourth pic.twitter.com/WzLjBjspuT
Credit - X/@NASA
Scientists recently spied another solar system named Trappist-1 for searching alien lives. This system is known as one of the most promising places to detect alien life. Trappist-1 is a cool red dwarf star located approximately 40 light years away. Several planets also orbit around it and researchers believe that conditions might be helpful for origin of life. After a long 28 hours of scanning, using the Allen Telescope Array, the researchers found only some signals, however, none them came from non-human origin. Among millions of potential signals, only 11,000 were seen as promising, which would be analyzed further.
Warning Bells: Water Scarcity Could Halve Global Food Production

As per Global Commission on the Economics of Water report: “decades of collective mismanagement and undervaluation of water around the world have damaged freshwater and land ecosystems and allowed for the continuing contamination of water resources. We can no longer count on freshwater availability for our collective future.”
The natural process of water moving between the earth and the atmosphere is crucial for sustaining life on the earth. The process involves the evaporation of water, cloud formation, followed by rainfall and snowfall. However, the globe is facing the consequences of disruption of this delicate balance. “Nearly 3 billion people and more than half of the world's food production are now in areas where total water storage is projected to decline,” stated the report. This can lead to an economic damage equivalent to 8% of GDP by 2050.
The report recommended to reform the economic approach to water, requesting governments to implement water policies for sustainable use.