
Here are today’s most important updates from the realm of Science and Space.
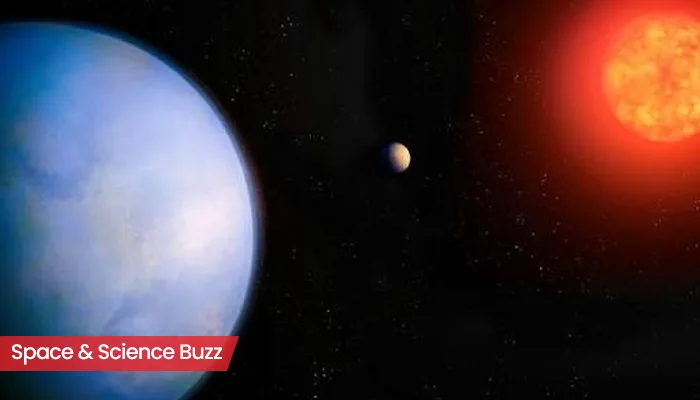
India’s Space Triumph: A Super-Sized Exoplanet Takes the Spotlight
A team of researchers from the Physical Research Laboratory (PRL) in Ahmedabad have made a stunning discovery outside the Solar System. The newly detected planet, dubbed TOI-6038A b, is a dense sub-Saturn size with a mass of 78.5 Earth masses and a radius of 6.41 Earth radii in a wide binary system. The planet orbits a bright, metal-rich F-type star every 5.83 days in a circular orbit. An F-type star is a type of star that is hotter and brighter than our Sun but not as extreme as the hottest stars in the universe. It falls between A-type (hotter) and G-type (like our Sun) in the star classification system.
Shaken and Shifted! Massive 2024 Earthquake Redraws the Map

On January 1, 2024, when the world celebrated the beginning of a new year, a massive magnitude 7.5 earthquake shook the Noto Peninsula, Japan. Over a year later, scientists have revealed how it led to major topological and geographical changes in the region. Scientists used radar images from Japan’s ALOS-2 satellite to create maps showing how the Noto Peninsula earthquake changed the land. The images revealed that parts of the northern coast rose more than four meters, creating new terraces. The entire North Noto region moved westward, and slopes in the mountains shifted. Some large landslides, stretching for kilometers, were only visible through satellite analysis. The study uncovered the details of how massive earthquakes can lead to drastic changes to the landscape in a short span of time.
Deep Freeze Tremors: Never-Before-Seen ‘Ice Quakes’ Detected in Greenland

In a first, researchers have recorded countless "ice quakes" that sporadically shake the Greenland Ice Sheet. These quakes may explain the jerky way that the island's frozen rivers move downstream toward the sea. Similar to earthquakes, ice quakes are seismic events that can happen in ice when it fractures and two slabs grind against each other. Ice quakes can trigger other ice quakes like dominoes, and thereby propagate horizontally over large distances. Meanwhile, the Greenland Ice Sheet is the largest ice sheet in the Northern Hemisphere, covering approximately 80% of Greenland's landmass. Meltwater from the Greenland Ice Sheet is already the biggest global source of sea level rise, accounting for a 0.6-inch (1 centimeter) increase since the 1990s.
California’s Slow Descent: NASA Uncovers a Global Sinking Trend

A new NASA-led study has revealed how California is losing ground on an annual basis as coastal water moves in. The team used satellite radar to track more than a thousand miles of California coast rising and sinking in new detail. They found that the centre of California, parts of the Central Valley, is sinking as much as 8 inches, or 20 centimetres, per year due to land motion is influenced by groundwater withdrawal. According to NASA, the elevation changes may seem small amounting to fractions of inches per year, but they can increase or decrease local flood risk, wave exposure, and saltwater intrusion. The event is not limited to California, similar sinking events have been observed across the world.


.webp)
.WEBP)
.WEBP)
.webp)
.webp)


.webp)
.webp)
.webp)